microscope magnification equation|microscope magnification examples : Bacolod Magnification = Eyepiece Magnification X Objective Magnification. Microscopes magnify or enlarge the image under inspection and enables the human eye to see things we would never be able to see.
Best Festivals in Mandaluyong, Metro Manila, Philippines - Pasinaya Festival, San Juan Town Fiesta, International Silent Film Festival, Wanderland Music & Arts Festival, Brasilipinas, Korean Film Festival, NexCon, Fête de la Musique Manila, Eiga Sai, Japanese Film Festival, Cine Europa
microscope magnification equation,The magnification of a microscope can be calculated using the following formula: Total Magnification = Objective Power x Eyepiece Power. Enter Objective Power: x. Enter Eyepiece Power: x. Calculate. Reset. The objective lens is the lens . Physics ⋅. Sound & Light (Physics): How are They Different? How to Calculate Total Magnification of a Microscope or Telescope. •••. Updated April 09, 2023. By Karen G Blaettler. Microscopes magnify the . The magnification of the microscope is the product of the linear magnification \(m^{obj}\) by the objective and the angular magnification \(M^{eye}\) by .Step 1: Check that units in magnification questions are the same Remember that 1mm = 1000µm. 2000 / 1000 = 2, so the actual thickness of the leaf is 2 mm and the drawing .
Equation. Magnification can be worked out from a photograph or drawing using the equation below: The same unit of measurement should be used when making the .Magnification = Eyepiece Magnification X Objective Magnification. Microscopes magnify or enlarge the image under inspection and enables the human eye to see things we would never be able to see. m = mome, (26.4.14) (26.4.14) m = m o m e, where mo m o is the magnification of the objective and me m e is the magnification of the eyepiece, such as . Introduction: A microscope is an instrument that magnifies an object so that it may be seen by the observer. Because cells are usually too small to see with the . Key Points. Magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. Resolution is the ability to distinguish . Understand the optics of a simple magnifier. Characterize the image created by a simple magnifier. The apparent size of an object perceived by the eye depends on .
microscope magnification equation The Formula for Total Microscope Magnification. When using a microscope, it is important to understand how to calculate the total magnification. Total magnification refers to the degree to which an object is enlarged when viewed through a microscope. It is determined by the combined magnification of the microscope’s .
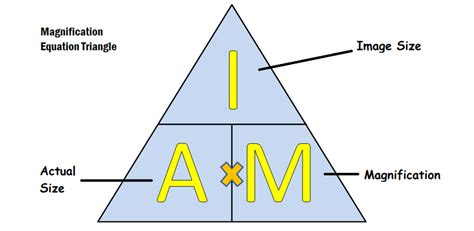
Calculating magnification and specimen size using millimetres as units. Magnification is calculated using the following equation: Magnification = Image size ÷ Actual size. A better way to remember the equation is using an equation triangle: Magnification equation. Rearranging the equation to find things other than the magnification becomes . Now, finally the useful range of magnification can be defined by combining Equations 9 and 10: Equ. 11. Thus, the useful range of magnification is between 1/6 and 1/3 of the microscope system resolution. High magnification. Modern camera sensors have pixels sizes in the 1 to 6 µm range, well below 10 µm.Magnification: Magnifying/Focusing. Figuring Total Magnification. Magnifying Objects/ Focusing Image: When viewing a slide through the microscope make sure that the stage is all the way down and the 4X scanning objective is locked into place.; Place the slide that you want to view over the aperture and gently move the stage clips over top of the slide to .
T = M x N. Using the example from Step 1 and Step 2, T = 10,000 x 100 = 1,000,000x. To calculate the magnification power of the electron microscope, you need to know the magnification of the objective lens and the ocular lens. By multiplying these values, you can find the total magnification power of the instrument.
Microscopes were first developed in the early 1600s by eyeglass makers in The Netherlands and Denmark. The simplest compound microscope is constructed from two convex lenses as shown schematically in Figure 26.16.The first lens is called the objective lens, and has typical magnification values from 5× 5× to 100× 100×.In standard .
A convex lens used for this purpose is called a magnifying glass or a simple magnifier. Figure 2.8.2: The simple magnifier is a convex lens used to produce an enlarged image of an object on the retina. (a) With no convex lens, the object subtends an angle θobject from the eye. (b) With the convex lens in place, the image produced by the .
Multiply the magnification of the lenses together. For example, if the eyepiece magnification is 10x and the objective lens in use has a magnification of 4x, the total magnification is: 10 \times 4 = 40\text {x} 10 ×4 = 40x. The total magnification of 40 means that the object appears forty times larger than the actual object.The above equation can be rearranged in order to calculate the actual length of the cell and the magnification used as well as the length of the image. A ctual Length = length of the I mage .

Magnification: Magnifying/Focusing. Figuring Total Magnification. Magnifying Objects/ Focusing Image: When viewing a slide through the microscope make sure that the stage is all the way down and the 4X scanning objective is locked into place.; Place the slide that you want to view over the aperture and gently move the stage clips over top of the slide to .The Concept of Magnification. A simple microscope or magnifying glass (lens) produces an image of the object upon which the microscope or magnifying glass is focused. Simple magnifier lenses are bi-convex, . Where: – ( f) is the focal length of the lens – ( d_o ) is the object distance – ( d_i) is the image distance Once we have the lens equation, we can calculate the magnification using the formula: Where: – ( M) is the magnification Zoom Lens Calculation. To illustrate the calculation of zoom lens magnification, let’s consider an .
Based on the chart above we would calculate digital magnification by using 482.6mm / 8.00 = 60.325. Now we can find the total on-screen magnification by multiplying optical magnification x digital . Key Points. Magnification is the ability to make small objects seem larger, such as making a microscopic organism visible. Resolution is the ability to distinguish two objects from each other. Light microscopy has limits .
microscope magnification examplesMost objectives in the magnification range between 60x and 100x (and higher) are designed for use with immersion oil. By examining the numerical aperture equation above, we find that the highest theoretical numerical aperture obtainable with immersion oil is 1.51 (when sin (µ) = 1). In practice, however, most oil immersion objectives have a . TEM: An Overview. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a form of microscopy which in which a beam of electrons transmits through an extremely thin specimen, and then interacts with the specimen when passing through it. The formation of images in a TEM can be explained by an optical electron beam diagram in Figure 8.2.1 8.2.There is a wealth of information inscribed on the objective barrel. Briefly, each objective has inscribed on it the magnification (e.g. 10x, 20x or 40x etc.); the tube length for which the objective was designed to give its finest images (usually 160 millimeters or the Greek infinity symbol); and the thickness of cover glass protecting the specimen, which was assumed . Introduction: A microscope is an instrument that magnifies an object so that it may be seen by the observer. Because cells are usually too small to see with the naked eye, a microscope is an essential tool in the field of biology. In addition to magnification, microscopes also provide resolution, which is the ability to distinguish two nearby .
microscope magnification equation|microscope magnification examples
PH0 · resolution microscope definition
PH1 · microscope magnification examples
PH2 · microscope magnification chart
PH3 · magnification formula
PH4 · levels of magnification microscope
PH5 · formula for microscope magnification
PH6 · equation to work out magnification
PH7 · Iba pa